Author: Ian
Date Posted: Feb 23, 2024
Last Modified: Nov 29, 2024
XML API data in Snowflake using a File Format
Load, flatten and transform XML data using a Snowflake File Format.
These Data Productivity Cloud pipelines extract XML data from a public RSS feed, load it into Snowflake using a File Format, and then transform and flatten it. An RSS feed is a simple REST API.
Extract and Load XML data
Start with the XML RSS demo - Extract and Load pipeline. It extracts data from a public AWS RSS blog feed https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/feed/, and creates a file in S3 storage containing the XML. Before running the pipeline you must edit it to replace your-bucket-name in the properties of the Data Transfer and the S3 Load components.
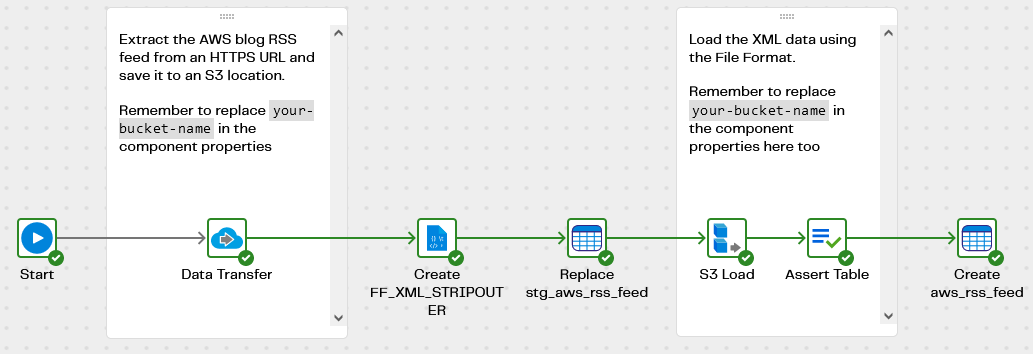
The File Format object is named FF_XML_STRIPOUTER and has the following settings:
- File Type XML
- Strip Outer Element True. This removes the outermost
<rss>element, leaving a list of<item>s inside a<channel>
The destination Snowflake table is named stg_aws_rss_feed. It contains semi-structured data, and so has just one VARIANT column named channel.
An S3 Load component references the File Format, and loads the data into Snowflake. The entire XML document is loaded into one record, and the Assert verifies that this has successfully happened at runtime.
Every few days the RSS feed will update and the source data will change. So the stg_aws_rss_feed table is relatively short term. The permanent destination table is named aws_rss_feed. It has relational columns GUID, TITLE, DESCRIPTION and PUBDATE so a transformation pipeline is needed to feed data into it.
Flatten and Transform XML data
Data transformation - including flattening - happens inside Snowflake, managed by the XML RSS demo - Transform pipeline. It takes the single record from stg_aws_rss_feed and runs a LATERAL FLATTEN to un-nest the <item> elements from the XML. This example takes a more high code approach than the UDF and Extracted Nested Data from the companion XML UDF conversion example
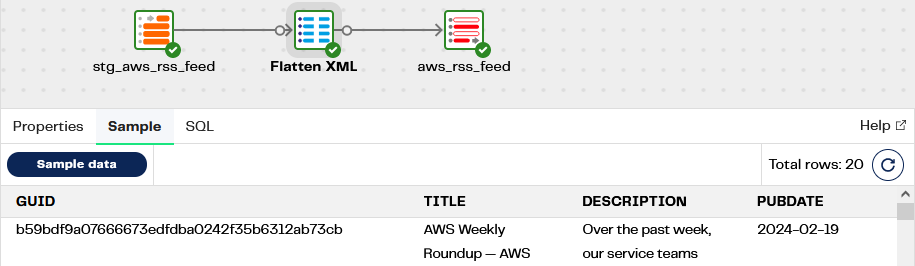
Note the following in the Flatten XML component properties:
- The dollar sign operator, expressed as
"channel":"$"parses the XML - XMLGET functions pick out the XML tags of interest
- Snowflake
::operators CAST the XML data into strings or dates - The LATERAL FLATTEN join changes the granularity from one record to however many
<item>elements are present (20 in the screenshot above). This is rather like a Wide to Narrow transpose
Now that the semi-structured data has been relationalized, a Table Update component performs the MERGE to the permanent destination table aws_rss_feed. Every <item> in the RSS contains a guid identifier which is used to distinguish between inserts and updates.
Downloads
Licensed under: Matillion Free Subscription License